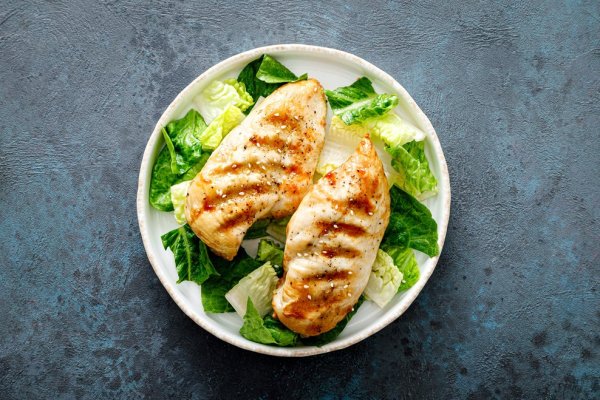
Omega-3 is not tolerant of high temperature, so is it best to eat raw fish tablets? Professor reveals the best way to cook fish meat

Reader Mr. Zhou used the website’s "Contact Me" on 2023-12-3 to inquire:
"Teacher, I would like to ask: 1. The teacher said that the ALA conversion rate of plant-based omega3 is not high, and according to current research, it is not beneficial to humans. Can you think that there is no need for special supplementation? 2. omega3 is not resistant to high temperatures. Is there not much leftover omega3 except boiling and steaming, roasting and frying? Or Can you ignore it? Thank you teacher. It seems that it is better to eat fish raw fish slices ……"Regarding whether ALA is beneficial to humans, I have discussed several times, such as the re-discussion of "Asia seed oil, fish oil" published on 2017-2-13 and the Omega-3 fatty acid ALA/EPA/DHA/DPA published on 2023-6-29.
Since the readers still have questions, I would like to read Omega-3 Fatty Acids: An Essential Contribution: "ALA can be converted to EPA and DHA, but the conversion rate is limited, so we still don’t know whether single ALA can provide the best intake of omega-3 fatty acids. ”
Regarding the impact of cooking methods on EPA/DHA, I would like to read a few articles first, and then I will summarize it in the end.
2002: Comparison of the effects of microwave cooking and conventional cooking methods on the composition of fatty acids and fat quality indicators in herring. Regardless of the common operation or the use of microwave ovens, it will not lead to a decrease in the proportion of Omega-3 fatty acids in the total fatty acids.
2010: Effect of different types of heat processing on chemical changes in tuna. Cooked pork chops had minimal loss of EPA and DHA, followed by microwave heating. The can completely destroy these fatty acids. In fried fish, EPA and DHA lost 70% and 85% respectively.
2018: Cooking methods affect total fatty acid composition and retention of DHA and EPA in selected fish fillets (cooking methods affect total fatty acid composition and retention of DHA and EPA in selected fish fillets). Compared with raw fish slices (119), DHA + EPA is the highest reserved in yellow fish slices from the cooking method (112), followed by foil baking (108), roasting (99) and frying (93). Compared with raw fish slices, steaming and baking with aluminum foil paper can preserve the DHA and EPA content in all types of cooked fish slices studied. Frying and roasting methods showed a significant reduction in DHA and EPA content in all fish slices compared to steaming and foil baking.
2021: The effects of cooking salmon sous-vide on its antithrombotic properties, lipid profile and sensory characteristics. This gentle cooking has a beneficial effect on maintaining antithrombotic and cardiac protection properties. (Note: For low-vapor cooking, please see Shufei cooking, bacterial breeding?)
2022: Review on retention of long-chain omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (EPA and DHA) in fish as affected by cooking methods [A summary of the effects of cooking methods on the retention of medium-long chain omega-3 in fish and fatty acids (EPA and DHA) in fish as affected by cooking methods]. Baking, roasting and steaming are recommended ways to cook healthy. Although frying is more acceptable in flavor and structure than baking and other cooking methods, it is not recommended for those who restrict their dietary fat intake due to diet and health problems.
2023: Effect of Different Cooking Methods on Lipid Content and Fatty Acid Profile of Red Mullet (Mullus barbatus). The proportion of EPA+DHA in total fatty acids: raw fish (25.5%). Oven cooking (19.6%) and frying (4.99%).
Therefore, in addition to canning and frying, general cooking methods (steaming, boiling, microwave, frying, baking, roasting, and fertilizing) can keep EPA and DHA to a relatively good level.
Recent Note: Two face friends were surprised that the canned fish would lose omega-3. Regarding this point, I would like to refer to the information provided by reader Elliot:
Can head is a question, canning The process (bacterial method, etc.) and heating method can make the canned fish products highly retain fish oil, or the fish oil loss rate is extremely high. Personally, I often eat fish cans (龙文, sardine, etc.), and they are all fish cans. Most imported from Southeast Asia are fried, most imported from Japan, South Korea and South Europe and Taiwan are steamed, and most imported from Northern Europe and East Europe are smoked (delicious, but a bit expensive). Whether to keep fish oil is one thing (I don’t care specifically). What you may need to pay attention to in canned fish is: whether you have added too much sauce (oil, salt, sugar), the following is for reference.
Aquatic tank head– Taiwan: sauce
– Fettie: sauce
– Japan and South Korea: sauce
– Mediterranean country: oil
– Northern Europe: Salt
* Notes: Reading content, added sugar and total heat
* Notes: Reading the weight of solids, non-content weight, for example: the same is 230 grams of tomato juice, the A-brand solids 120 grams, and the B-brand solids 150 grams, and the salt fish family. In addition, the fish fish cans are mostly Skipjack varieties, and the Western fish cans are commonly seen as Albacore varieties. The British NHS does not regard fish as fatty fish source, the American AHA regards fish as fatty fish source, Taiwan's smoke tiger Skipjack is a close relative of fish, and the fish oil content is actually not low. The fish oil content of fish in different varieties, sea areas and parts can also be far away. The fish varieties in East Asia (Japan and South Korea) in the Western Pacific are generally fatter. Just eat happily, don't think so much.
Original text: Omega-3: Is ALA beneficial? Are EPA/DHA afraid of high temperatures?Responsible editor: Gu Zihuan