Big impact! NVIDIA AI servers are rumored to be considering switching to LPDDR, and memory supply will continue to tighten next year

As memory manufacturers shift production capacity to high-end AI memory products, traditional memory is affected by a shortage. The research firm Counterpoint Research released a latest report stating that the industry is currently facing new problems because NVIDIA is switching to memory chips commonly used in smartphones in AI servers, which may double the price of server memory by the end of 2026.
According to Counterpoint's latest report "Memory Solutions for GenAI" quoted by Reuters, the industry is also facing a new problem. In order to reduce the power consumption of AI servers, NVIDIA decided to change the server memory from DDR5 used in general servers to LPDDR, a low-power memory commonly used in mobile phones and tablets. The agency pointed out that from a longer-term and broader perspective, as NVIDIA significantly increases the demand for LPDDR on the server side, advanced memory supply risks are rapidly spreading and beginning to affect the overall consumer electronics market.
Counterpoint believes that since each AI server requires more memory chips than a mobile phone, NVIDIA's decision may significantly increase the demand for LPDDR. In addition, Samsung, SK Hynix and Micron have concentrated their production capacity on high-bandwidth memory (HBM), resulting in a shortage of traditional DRAM products. The industry may not be able to cope with the sudden surge in demand.
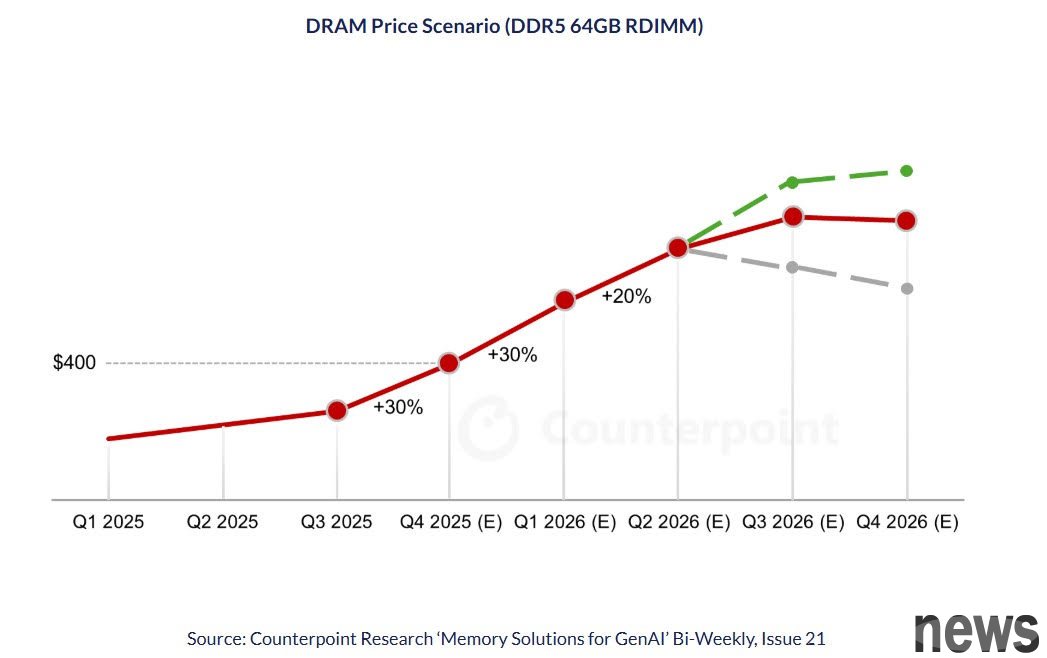
According to the report, memory prices are expected to increase by 30% in the fourth quarter of 2025 and by another 20% early next year. These gains will be added to the 50% gains already accumulated so far this year, keeping market pressures elevated. One of the key factors currently causing market distortion is that suppliers are shifting production capacity to more advanced memory in response to AI demand, resulting in an increasingly tight supply of LPDDR4.
At the same time, there is also a clear imbalance in the spot market: DDR5 used in servers and PCs costs about US$1.50 per Gb, while DDR4 used in consumer electronics costs as high as US$2.10, even higher than the advanced HBM3e's level of about US$1.70.
Counterpoint expects that the supply crunch in the low-end memory market may spread upward, as memory manufacturers must weigh whether to shift more production capacity to manufacturing LPDDR to meet NVIDIA demand. Research Director MS pointed out, "The real greater risk lies in advanced memory. As NVIDIA turns to LPDDR, its demand scale has become the same as that of first-tier smartphone brands, which has made it difficult for the global supply chain to quickly Absorbing the huge impact".
The agency also expects that the price of memory chips for servers will double by the end of 2026. As rising server memory prices have increased costs for cloud service providers and AI developers, and data center budgets are already tight due to GPU procurement and power upgrades, this may put greater pressure on data center budgets.
The current shortage mainly affects the entry-level price range of the smartphone market. Counterpoint senior analyst Ivan Lam pointed out that this wave of pressure may further extend to the entire smartphone and consumer electronics ecosystem. Taking mid-to-high-end models as an example, their BOM (bill of materials cost) may increase by more than 15%, compressing profit margins or inhibiting growth, and both are likely to occur at the same time.
Counterpoint expects that DRAM production by major memory suppliers will grow by more than 20% in 2026. Research director MS Hwang said that Samsung may readjust its expanded 1C process; SK Hynix is actively increasing production and increasing shipment targets; Changxin Memory (CXMT) may deliver a more impressive performance; and Micron, which has always focused on return on investment, is unlikely to adopt a conservative strategy in such a market atmosphere.
In addition, macro factors such as tariffs, geopolitics, and the job market will also deepen industrial uncertainty. Overall, restricted production capacity and rising prices have created a highly volatile market environment, which will force suppliers and manufacturers to face difficult choices.
Nvidia chip shift to smartphone-style memory to double server-memory prices by end-2026 – Counterpoint Further reading: DRAM surge impact! Foreign media said it may prompt AMD to increase GPU prices The U.S. is expected to nod to allow chip exports to Saudi Arabian AI startup Humain